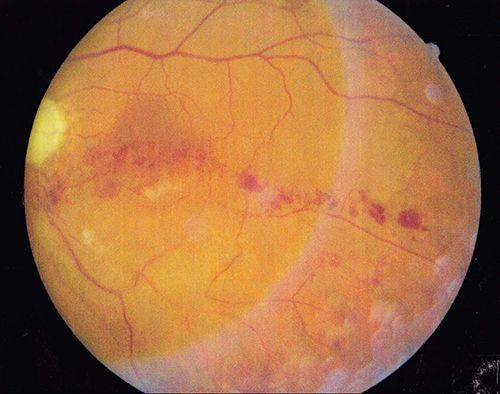
Retinal Vein Occlusion
What is Retinal Vein Occlusion?
The retina is sensitive tissue that requires blood flow from arteries and veins. A blockage or occlusion of a vein results in a retinal vein occlusion.
The most common cause of a blockage is one vessel pressing down on another and causing it to narrow and occlude. Occasionally, a blockage can occur from a blood clot. A retinal vein occlusion may result in the leakage of fluid from the blood vessels. This fluid causes the retina to swell and thicken. The swelling of the retina is called macular edema, and it can cause blurry vision or loss of vision.
An additional complication of a retinal vein occlusion is the growth of abnormal new blood vessels. These blood vessels can grow in the back of the eye and bleed. Or they can grow in the front of the eye (on the iris or colored part of the eye) and cause the eye pressure to go up. When the eye pressure rises too high, it can cause permanent damage to the vision and pain.
What are causes of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
Risk factors for Retinal Vein Occlusion include:
- Diabetes
- Glaucoma (increased eye pressure)
- High Blood Pressure
- Blood vessel diseases or inflammations (vascular disease)
What are the Symptoms of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
Symptoms of Retinal Vein Occlusion include:
- Blurriness or loss of vision
- Floaters
- Eye pain
It is very important to be evaluated by an ophthalmologist right away if you have any of these symptoms. Without treatment, a retinal vein occlusion can cause blindness.
How is Retinal Vein Occlusion diagnosed?
Dilating drops to dilate (widen) the pupil are necessary to examine the inside of the eye with a special lens.
Two different tests are often used to determine the extent of damage from a retinal vein occlusion.
These are:
1) Fluorescein Angiography — Special pictures that look at the blood flow to the retina. A yellow dye (called fluorescein) is injected into a vein, usually in your arm or hand. A camera is then used to take photos of the inside of you eye.
2) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) — A machine that scans the retina and provides detailed images of the retina, like a virtual biopsy. This scan helps your doctor identify swelling and leakage of fluid in the retina.
How is Retinal Vein Occlusion treated?
Treatment is based on the extent of damage in the eye.
A retinal vein occlusion can cause vision loss or blurry vision. Treatments consist of medication injections in the eye and sometimes laser treatment. It is also important to control other health problems like diabetes and high blood pressure. Regular follow up examinations need to be maintained for optimum visual results.
Advanced Retina Associates offices are located in
Orange City and
Port Orange
Advanced Retina Associates, Dr Lieb.
Site Design by Infinity Medical Marketing.